10 XForms Actions
All form controls defined in this specification have a set of common behaviors that encourage consistent authoring and look and feel for XForms-based applications. This consistency comes from attaching a common set of behaviors to the various form controls. In conjunction with the event binding mechanism provided by [XML Events], these handlers provide a flexible means for forms authors to specify event processing at appropriate points within the XForms user interface. XForms actions are declarative XML event handlers that capture high-level semantics. As a consequence, they significantly enhance the accessibility of XForms-based applications in comparison to previous web technologies that relied exclusively on scripting.
NOTE: This example is based on the XML Events specification [XML Events], which is proceeding independently from XForms, and thus might be slightly incorrect.
<xforms:button> <xforms:caption>Reset</xforms:caption> <xforms:resetInstance ev:event="xforms:activate"/> </xforms:button>
This example recreates the behavior of the HTML reset button, which this specification does not define as an independent form control.
For each built-in XForms action, this chapter lists the following:
Name
Description of behavior
XML Representation
Sample usage
All elements defined in this chapter explicitly allow global attributes from the XML Events namespace, and apply the processing defined in that specification in section 2.3 [XML Events].
10.1 dispatch
This action dispatches an XForms Event to a specific element identified
by the target attribute. Two kinds of event can be dispatched:
One of the predefined XForms events (i.e., xforms:event-name), in which case the bubbles and cancelable attributes are ignored and the standard semantics as defined in the Processing model apply.
An event created by the XForms author with no predefined XForms semantics and as such not handled by default by the XForms processor.
dispatch><dispatch name = xsd:NMTOKEN target = xsd:IDREF bubbles = xsd:boolean : true cancelable = xsd:boolean : true />
name = xsd:NMTOKEN - required name of the event to dispatch.
target = xsd:IDREF - required reference to the event target.
bubbles = xsd:boolean : true - boolean indicating if this event bubbles—as defined in DOM2 events.
cancelable = xsd:boolean : true - boolean indicating if this event is cancelable—as defined in DOM2 events.
10.2 refresh
This action dispatches an xforms:refresh event. This action results in the XForms user interface being
refreshed, and the presentation of user interface controls being
updated to reflect the state of the underlying instance data --see
4.3.15 xforms:refresh
refresh><refresh/>
10.3 recalculate
This action dispatches an xforms:recalculate event. As a result, instance data nodes whose values need to be
recomputed are updated as specified in the processing model --see
4.3.17 xforms:recalculate.
recalculate><recalculate/>
10.4 revalidate
This action dispatches an xforms:revalidate event. This results in the instance data being revalidated as specified
by the processing model --see 4.3.16 xforms:revalidate
revalidate><revalidate/>
10.5 setFocus
This action sets focus to the form control referenced by the
idref attribute by dispatching an xforms:focus event. Note that this event is implicitly invoked to implement XForms
accessibility features such as accessKey.
setFocus><setFocus idref = xsd:IDREF />
idref = xsd:IDREF - required reference to a form control
Setting focus to a repeating structure sets the focus to the member represented by the repeat cursor.
10.6 loadURI
This action traverses the specified XLink.
loadURI><loadURI
(single node binding attributes)
xlink:href = xsd:anyURI
xlink:show = ("new" | "replace" | "embed" | "other" | "none")
/>(single node binding attributes) - Selects the instance data node containing the URI.
xlink:href - optional URI to load.
xlink:show - optional link behavior specifier.
Either the single node binding attributes, pointing to a URI in the
instance data, or the attribute xlink:href are required. If both are
present, the action has no effect.
Possible values for attribute xlink:show have the following
processing for the document (or portion of a document) reached by traversing
the link:
- new
The document is loaded into a new window (or other presentation context). Form processing in the original window continues.
- replace
The document is loaded into the current window. Form processing is interrupted, exactly as if the user had manually requested navigating to a new document.
- embed
The document is incorporated into the current window in an application-specific manner. Form processing continues.
- other
The document is loaded in an application-specific manner. The application should look for other markup present in the link to determine the appropriate behavior.
- none
The document is loaded in an application-specific manner. The application should not look for other markup present in the link to determine the appropriate behavior.
10.7 setValue
This action explicitly sets the value of the specified instance data node.
setValue><setValue (single node binding attributes) value = XPath expression > <!-- literal value --> </setValue>
(single node binding attributes) - Selects the instance data node where the value is to be stored.
value = XPath expression - XPath expression to evaluate, with the result stored in the selected instance data node.
The element content of setValue specifies the literal value to
set; this is an alternative to specifying a computed value via attribute
value. The following two examples contrast these approaches:
<setValue bind="put-here" value="a/b/c"/>
This causes the string value at a/b/c in the instance data
to be placed on the single node selected by the bind element with
id="put-here".
<setValue bind="put-here">literal string</setValue>
This causes the value "literal string" to be placed on the single node selected
by the bind element with id="put-here".
If neither a value
attribute nor text content are present, the effect is to set the value of the selected
node to the empty string ("").
10.8 submitInstance
This action initiates submit processing by dispatching an xforms:submit event. Processing of event xforms:submit is defined in the processing model—see 4.4.1 xforms:submit.
submitInstance><submitInstance submitInfo = xsd:IDREF />
id = xsd:ID - optional unique identifier.
submitInfo = xsd:IDREF - optional reference to asubmitInfoelement.
Note:
This XForms Action is a convenient way of expressing the following:
<dispatch target="mysubmitinfo" name="submitInstance"/>
10.9 resetInstance
This action initiates reset processing by dispatching an xforms:reset event to the specified model. Processing of event xforms:reset is defined in the processing model—see 4.3.18 xforms:reset.
resetInstance><resetInstance model = xsd:IDREF />
model = xsd:IDREF - Selection of instance data for reset, defined in 8.12.3 Nodeset Binding Attributes
10.10 setRepeatCursor
This action marks a specific item as current in a repeating sequence (within 9.3 repeat).
setRepeatCursor><setRepeatCursor repeat = xsd:IDREF cursor = XPath expression that evaluates to number />
repeat = xsd:IDREF - required reference to a repeat
cursor = XPath expression that evaluates to number - required 1-based offset into the sequence.
10.11 insert
This action is used to insert new entries into a homogeneous
collection, e.g., a set of items in a shopping cart. Attributes of action
insert specify the insertion in terms of the collection in which a new
entry is to be inserted, and the position within that collection where the new
node will appear. The new node is created by cloning the final member of the
homogeneous collection specified by the initialization instance data. In this
process, nodes of type xsd:ID are not copied. The rules for insert processing are as follows:
The homogeneous collection to be updated is determined by evaluating binding attribute
nodeset.The corresponding node-set of the initial instance data is located to determine the prototypical member of the collection. The final member of this collection is cloned to produce the node that will be inserted. Finally, this newly created node is inserted into the instance data at the position specified by attributes
positionandat.Attribute
atis evaluated to determine the insertion index—a numerical value that is the index into the node-set. Attributepositionspecifies whether the new node is inserted before or after this index.The rules for selecting the index are as follows:
The return value of the XPath expression in attribute
atis processed according to the rules of the XPath functionround(). For example, the literal1.5becomes2, and the literal'string'becomesNaN.If the result is
NaN, the insert operation has no effect.If the result is not a valid index for the node-set, it is clipped to either
1or the size of the node-set, whichever is closer.
Finally, the cursor for any
repeatthat is bound to the homogeneous collection where the node was added is updated to point to the newly added node.
This action results in the insertion of newly created data
nodes into the XForms data instance. Such nodes are constructed as defined in
the initialization section of the processing model—see
4.2 Initialization Events. Following the insertion of the newly created node
into the instance data, events xforms:recalculate, xforms:revalidate and xforms:refresh are triggered in sequence. As an example, this causes the instantiation
of the necessary user interface for populating a new entry in the underlying
collection when used in conjunction with repeating structures
9.3 repeat.
insert><insert (node-set binding attributes) at = XPath expression position = "before" | "after" />
(nodeset binding attributes) - Selection of instance data nodes, defined in 8.12.3 Nodeset Binding Attributes
at - required XPath expression evaluated to determine insert location.
position - required selector if insert before/after behavior.
An example of using insert with a repeating structure is
located at 9.3 repeat. Note that XForms Action
setValue can be used in conjunction with insert to provide
initial values for the newly inserted nodes.
10.12 delete
This action deletes nodes from the instance data. The rules for delete processing are as follows:
The homogeneous collection to be updated is determined by evaluating binding attribute
nodeset. If the collection is empy, the delete action has no effect.The
n-th node is deleted from the instance data, wherenrepresents the number returned from node-set index evaluation, defined in 10.11 insert.If the last item in the collection is removed, the cursor position becomes 0. Otherwise, the cursor will point to the new
n-th item.
This action results in deletion of nodes in the instance
data. Following the specified deletion, events xforms:recalculate, xforms:revalidate and xforms:refresh are triggered in sequence. As an example, this causes the destruction
of the necessary user interface for populating a deleted entry in the
underlying collection when used in conjunction with repeating structures
9.3 repeat.
delete><delete (node-set binding attributes) at = XPath expression />
(nodeset binding attributes) - Selection of instance data nodes, defined in 8.12.3 Nodeset Binding Attributes
at - XPath expression evaluated to determine insert location.
An example of using delete with a repeating structure is
located at 9.3 repeat.
10.13 toggle
This action selects one possible case from an exclusive list
of choices e.g., encapsulated by switch see
9.2 switch, by:
Dispatching an
xforms:deselectevent to the currently selected item.Dispatching an
xform:selectevent to the item to be selected.
toggle><toggle case = xsd:IDREF />
case = xsd:IDREF - required reference to a case section inside the conditional construct
The toggle action adjusts all selected attributes on
the affected cases to reflect the new state.
10.14 script
This action encapsulates an event handler authored in the specified
scripting language. The handler may be inline,
i.e., as PCDATA content of element script; alternatively it may be
contained in an external resource and referred to via XML-events attribute
ev:handler. Optional attribute role serves as
documentation for the handler.
script><script type = xsd:string role=xsd:string > <!-- #CDATA --> </script>
type = xsd:string - required mime-type identifier of scripting language.
role = xsd:string - Optional descriptive text documenting the contained script.
10.15 message
This action encapsulates a message to be displayed to the user.
message><message (single node binding attributes) xlink:href = xsd:anyURI level = "ephemeral" | "modeless" | "modal" > <!-- mixed content --> </message>
(single node binding attributes) - optional attributes that point to the instance data for a string message.
xlink:href = xsd:anyURI - optional specifier of an external resource for the message.
level - required message level identifier.
The message specified can exist in instance data, in a remote document,
or as inline text. If multiple captions are specified in this element, the
order of preference is: ref, xlink:href, inline.
A graphical browser might render an ephemeral message as follows:
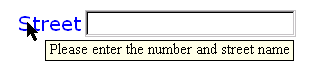
A graphical browser might render a modeless message as follows:
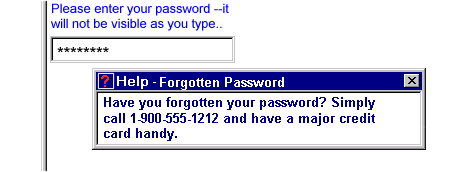
A graphical browser might render a modal message as follows:
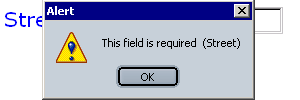
10.16 action
Action action is used to group multiple actions.
action><action > <!-- Action handlers --> </action>
When using element action to group actions, care should be
taken to list the event on element action, rather than on the
contained actions.
<button>
<caption>Click me</caption>
<action ev:event="xforms:activate">
<resetInstance/>
<setValue/>
</action>
</button>
Notice that in the above example, ev:event="xforms:activate" occurs on element action. Placing ev:event="xforms:activate" on either or both of the contained actions will have no effect. This is
because the above example relies on the defaulting of XML-Event attributes
observer and handler. As defined in the XML-Events
specification, if both observer and handler attributes are omitted, then the
parent is the observer. Placing ev:event="xforms:activate" on the children of element action therefore causes element
action to become the observer for the individual actions.
Consequently, these actions will never be triggered since events arrive at
element button, not element action.